Controlling Nematodes in Young Almonds
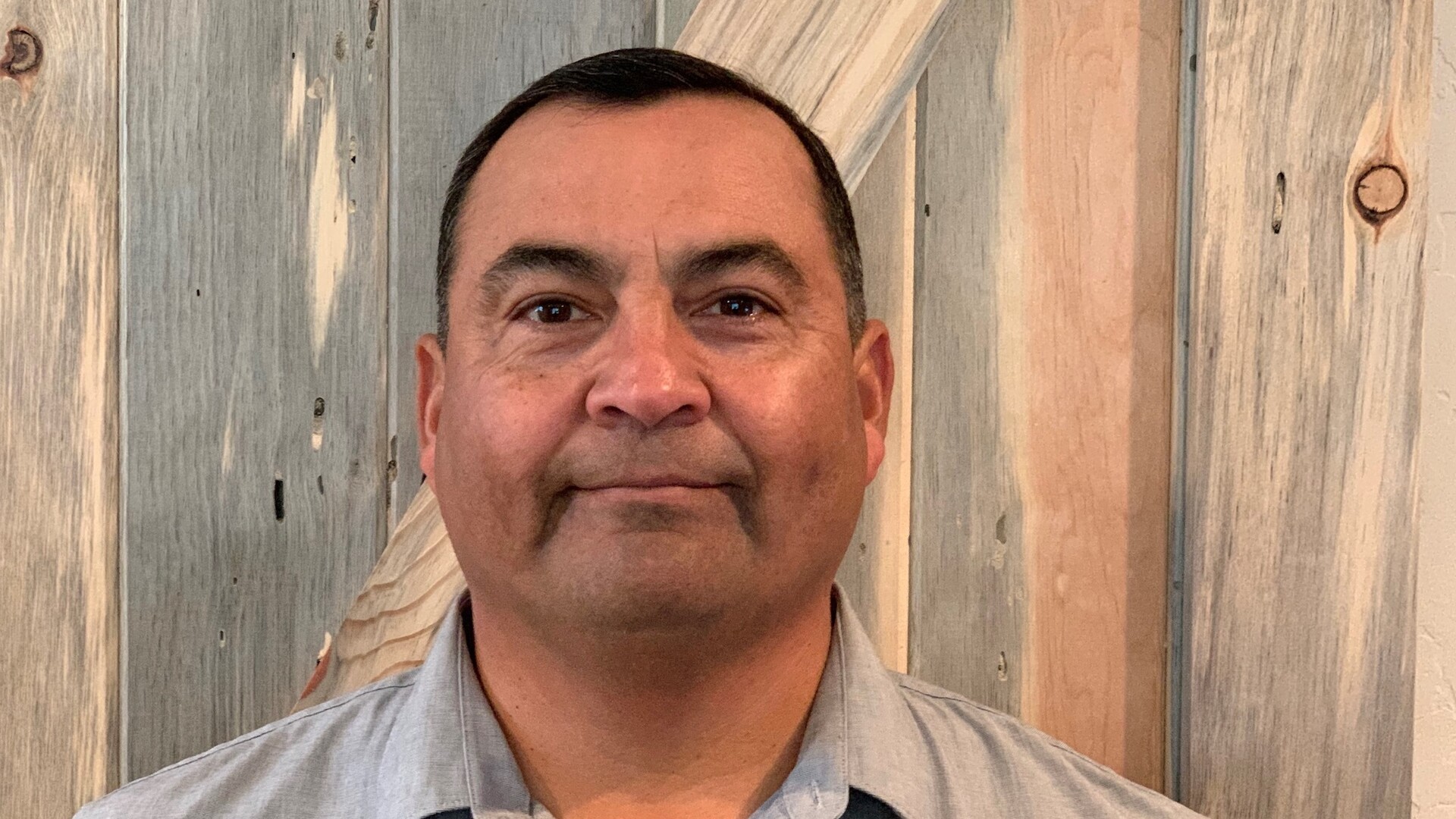
Protecting young almond trees from damaging nematodes, Manuel Jimenez is a customer business advisor, Bayer Crop Protection. His territory is Fresno and Tulare Counties.“Young almond trees are particularly susceptible to damage from nematodes because they have such a small root system when they're young,” said Jimenez. “And what we find is that you can also have problems with soil borne diseases on young trees like bacterial canker, or even Phytophthora root rot.”
Jimenez is talking about Bayer Crop Protection’s Velum One nematicide and he said it will indirectly protect those roots from other pathogens.
“Velum One is actually a contact nematicide, and it can indirectly affect the soil borne diseases by managing the nematodes who create damage on the roots. And it's that damage on the roots that create an entry point for those soil-borne diseases,” explained Jimenez.
The parasitic nematodes, that Velum One targets is root knot, lesion, and ring nematode. “These are the main nematode species that we find in soils where almonds are planted. The industry has developed rootstocks that offer some resistance to certain nematodes. Nemaguard, for example, is the dominant rootstock being used in almonds. And it has resistance to root knot nematode,” he said
“Because Nemaguard is a dominant rootstock, we actually don't find root knot nematode that often. So, the dominant ones that we see attacking almonds are ring nematode and lesion nematodes. And of course, Nemaguard does not offer protection against those species,” noted Jimenez said.
So, Velum One is important to control these dominant nematode species